Structure Of Atom
Atom -
As per the John Dalton's proposal in 1808 that the atom is the smallest indivisible particle of matter.
Atomic Radii -
Atomic radii are of the order of 10–8 cm (1Å) and radii of nuclei are nearly 10–13 cm.
Radius of atom  Radius of nucleus.
Radius of nucleus.
Electron -
- Electron was discovered through the study of Cathode rays (discovered by Zulius Plucker) and the name was proposed by Stoney.
- Charge of electron : It was determined by Mullikan by oil drop method as –1.602 × 10–19 coulombs or 4.803 × 10–10 e.s.u
- Mass of electron : It was found by J. J. Thomson as 9.11 × 10–28 g.
- Specific charge of electron : e/m ratio is called specific charge and was determined by Thomson as 1.76 × 108 coulombs/gm
- Radius of electron : It is of the order 10–15 cm.
- Density of electron : 2.17 × 1017 g/cc.
- Mass of electron at speed v is m =
- Atomic mass unit of electron : It is 0.0005486 amu
- Mass of one mole of electron : It is 0.55 mg
Cathode Rays -
- Cathode rays originated from cathode. And an Electrons were discovered by cathode ray experiment
- Cathode rays cast shadow of the object in their path.
- Cathode rays Rotate a mica wheel.
- Cathode rays are Deflected by electric and magnetic fields in a direction showing negative charge.
Proton -
Proton is discovered by Goldstein (1886) through perforated cathode rays experiment which showed the presence of anode or canal rays.
- Mass of Proton: It was found to be 1.672 × 10–24 g or 1.672 × 10–27 kg or 1.00728 amu. It is about 1837 times heavier than an electron.
- Charge of Proton: It carries unit positive charge 1.602 × 10–19 coulombs or 4.803 × 10–10 esu.
- Specific charge of Proton : It is 9.58 × 104 coulomb/gm. It varies with nature of gas and is maximum if H2 is used.
- Charge on 1 mole of proton is 96500 coulomb or 1 Faraday.
- Volume : The volume for proton is approximately 1.5 × 10–38 cm3.
Neutron -
It is discovered by Chadwick by bombarding Be or B atoms (sheet) with high speed 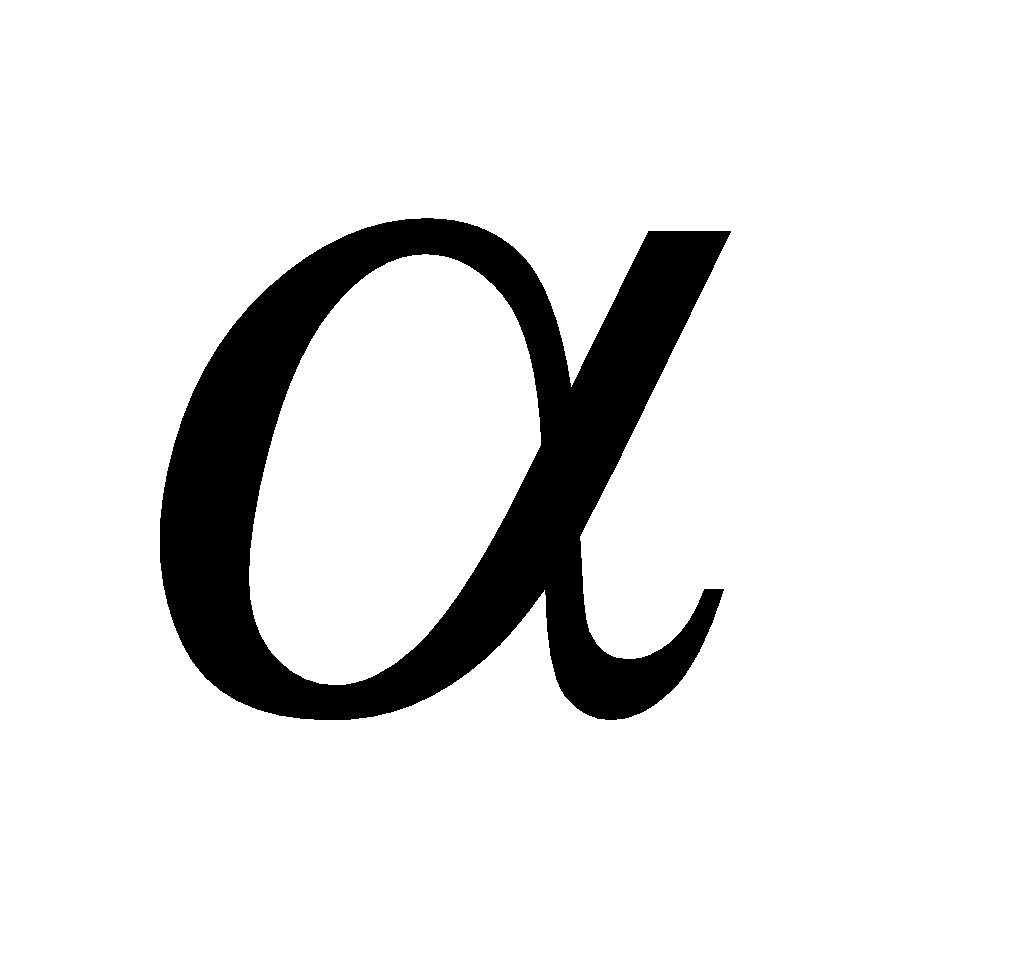 -particles
-particles
- Mass of Neutron: Mass is 1.675 × 10–24 gm or 1.675 × 10–27 kg or 1.00866 amu.
- It is heavier than proton by 0.18%.
- Density of Neutron : Density is 1.5 × 1014 g/cm3.
- Specific Charge of Neutron is ZERO.
- Stability of Neutron : It is least stable of all elementary particles present in an atom
- Disintegration of Neutron : Isolated neutron is unstable and disintegrates into electron, proton and neutrino.
- Among all elementary particles neutron is the heaviest and least stable.
